- By Ravindra Kumar
- 20 Jan, 2025
- Advertising
Advertising? Consider Product Life Cycle & Customer Buying Habits
This article provides valuable insights on how to create effective advertising for small businesses by considering both the product life cycle and customer buying habits. Here’s a breakdown of the key concepts discussed:
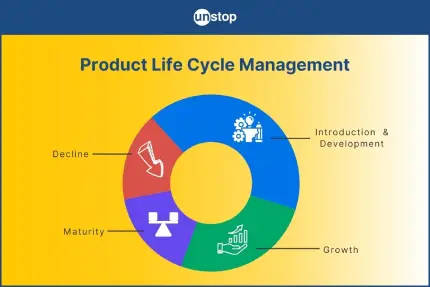
1. Understanding the Product Life Cycle
- Stages of Product Life Cycle: Classic marketing theory defines the life cycle of a product or service in five stages:
- Introduction – The product is new and unfamiliar to the market.
- Growth – The product gains traction and is rapidly accepted.
- Maturity – The product becomes an industry standard.
- Decline – Interest in the product begins to fade.
- Phase-out – The product is gradually phased out or becomes hard to find.
- Buyer Types in Each Stage: Different customer segments are more likely to purchase at each stage of the product life cycle:
- Innovative Adapters (a) – Early adopters who are willing to try new products or services and do their own research.
- Majority Adapters (b) – The larger group who follows recommendations, reads ads, or uses coupons.
- Stragglers (c) – The last group to adopt, often waiting until the product becomes the norm or is deeply discounted.
2. Adapting Advertising to Each Stage
- Targeting Innovators: When introducing a new product, your primary target market should be innovators (early adopters), who represent about 10 to 20 percent of the market. These customers are more likely to seek out and experiment with new offerings.
- Tip: Innovators often conduct research online, so ensuring your product is visible on the web is essential.
- Targeting Majority and Stragglers: Once the product gains momentum, advertising should shift to reach the larger majority of customers who make decisions based on reviews, recommendations, or discounts.
- Tip: Advertising should be educational and enticing, providing information that makes the product seem relevant and attractive to these followers.
3. The Importance of Repetition and Patience
- Building Awareness: Effective advertising should be repetitive to ensure that your product or service is always visible when customers are ready to make a purchase.
- Gradual Impact: Over time, good advertising can influence consumer buying habits. It’s essential to be patient and consistent with your messaging, as changing consumer behavior and attitudes can take time.
4. Key Takeaways:
- Know Your Audience: Tailor your advertising strategy based on the product’s life cycle stage and the buyer’s profile (innovators, majority adapters, or stragglers).
- Leverage Multiple Touchpoints: Reach your target audience through various means (e.g., ads, recommendations, research) to ensure maximum visibility and impact.
- Be Persistent: Successful advertising often requires repeated exposure and a long-term commitment to changing consumer habits.
Conclusion:
By understanding the product life cycle and aligning your advertising efforts with the buying habits of different consumer groups, you can increase the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns. Patience, repetition, and strategic targeting are key to influencing potential customers at the right time in their buying journey.